The ovary is full organ in the mammals, it is symmetrical and symmetrical and has the shape and magnitude of a large almond. It is located at the sides of the uterus, 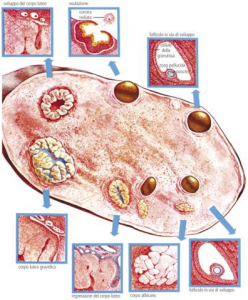 near the side walls of the female pelvis. Ovaries are important both from a reproductive point of view, as they produce female germ cells or oocytes, and from the endocrinologic point of view, as they secrete hormones. The ovary is covered externally by a superficial epithelium, which is fragile and thin but has a high regenerative capacity, useful in the follicle dehiscence; this epithelium rests on a dense connective layer called false albuginea that delimits the parenchyma of the organ, formed by a peripheral cortical zone and a central bone marrow. The cortical area is characterized by the presence of oophoreus follicles at various maturation stages, and are immersed in a connective tissue stroma rich in molten cells involved in follicular changes during the ovarian cycle. Oofori follicles are distinguished by: primordial, primary, secondary, vesicular, mature and atresive. The bone marrow is located at the center of the organ and is made up of connective ligament. It has a spongy appearance of red color, with the presence of several vessels passing through it, which form a kind of erectile tissue that fills with blood facilitates the outbreak of follicles. The medulla reaches the surface only at the eardrum. The presence of anti-ovarian antibody serum can lead to fertility problems.
near the side walls of the female pelvis. Ovaries are important both from a reproductive point of view, as they produce female germ cells or oocytes, and from the endocrinologic point of view, as they secrete hormones. The ovary is covered externally by a superficial epithelium, which is fragile and thin but has a high regenerative capacity, useful in the follicle dehiscence; this epithelium rests on a dense connective layer called false albuginea that delimits the parenchyma of the organ, formed by a peripheral cortical zone and a central bone marrow. The cortical area is characterized by the presence of oophoreus follicles at various maturation stages, and are immersed in a connective tissue stroma rich in molten cells involved in follicular changes during the ovarian cycle. Oofori follicles are distinguished by: primordial, primary, secondary, vesicular, mature and atresive. The bone marrow is located at the center of the organ and is made up of connective ligament. It has a spongy appearance of red color, with the presence of several vessels passing through it, which form a kind of erectile tissue that fills with blood facilitates the outbreak of follicles. The medulla reaches the surface only at the eardrum. The presence of anti-ovarian antibody serum can lead to fertility problems.
| Hemoagglutination | Latex agglutination | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sì | Sample Prediction | Yes | Yes for 30 minutes | Serum inactivation at 56 ° C | No | Yes | Prediction of controls | No | 90 minutes | Incubation | 3-4 minutes | CT-51-41 | REF | CT-51-21 | 40 | Test Number | 50 |



 Italiano
Italiano