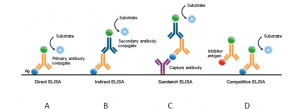
Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) combines the specificity of the antibodies with the sensitivity and simplicity of a typical enzymatic assay, using antibodies or antigens in conjunction with an enzyme. The ELISA tests allow to measure antigenic or antibody concentrations. Indeed, ELISA tests are basically of two types: using antibodies to detect the respective antigen, namely, using antigens to determine the presence of antibodies directed against them.
In general, a typical ELISA test consists of 5 steps:
- Antigen Adhesion to Micro Plate Wells;
- Block all antibody sites to prevent any false positive results;
- Addition of primary antibody to wells (eg monoclonal rabbit antibodies);
- addition of a secondary antibody (such as murine anti-IgG), conjugated to an enzyme (generally Rafano peroxidase, or HRPO)
- Addition of a chromogen that gives rise to a colored product in the presence of the enzyme, indicating the reaction (direct [A] or indirect [B] methods, higher coloring corresponds to greater concentration, in indirect methods [D ], higher coloring corresponds to lower concentration).There are several types of ELISA tests besides the schematic.



 Italiano
Italiano